In the coatings, adhesives, and sealants industries, curing agents play a pivotal role in transforming liquid resins into solid, high-performance films or bonds. Among various curing agents, polyisocyanate hardener has become a cornerstone material, valued for its ability to enhance resin performance through cross-linking reactions. Its unique combination of curing efficiency, chemical resistance, and versatility makes it indispensable in diverse industrial scenarios. Below are its core application advantages and features, illustrated with practical scenarios.
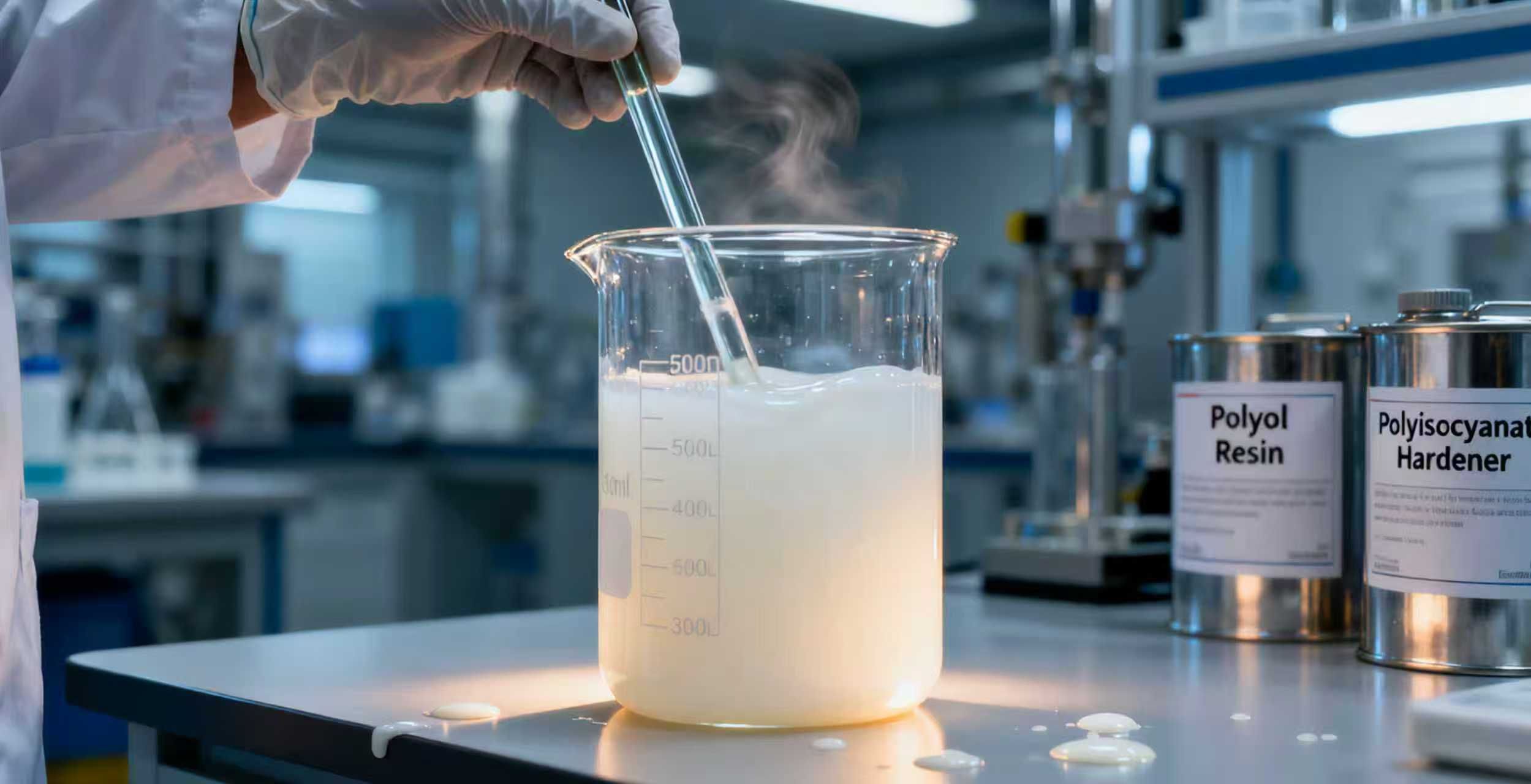

One of the most notable strengths of polyisocyanate hardener is its rapid curing speed and strong cross-linking capability, addressing a key pain point of traditional curing agents (which often require long drying times or high temperatures).
• Rapid Film Formation in Coatings: In automotive refinish coatings, polyisocyanate hardener reacts with hydroxyl-containing resins (e.g., acrylic, polyester) at room temperature, forming a dense cross-linked network within 30–60 minutes. This reduces the total curing time from hours (with amine-based curing agents) to under 2 hours, significantly boosting production efficiency.
• Instant Bonding in Adhesives: For structural adhesives used in aerospace components, polyisocyanate hardener enables "cold curing"—creating strong bonds between metal and composite materials in as little as 10 minutes, even at low temperatures (5–15℃), without needing ovens or pressure.
• Key Data: Tests show that coatings cured with polyisocyanate hardener achieve 90% of their ultimate hardness within 24 hours (per ASTM D2240), compared to 50% with conventional epoxy curing agents.
Polyisocyanate hardener forms a highly cross-linked film with low porosity, making it ideal for applications exposed to chemicals, solvents, or corrosive substances.
• Resistance to Industrial Chemicals: In chemical storage tank linings, coatings cured with polyisocyanate hardener withstand prolonged exposure to acids (e.g., 10% sulfuric acid) and solvents (e.g., ethanol) without blistering or peeling—unlike unmodified alkyd coatings, which degrade within weeks.
• Durability in Food Contact Scenarios: For food processing equipment coatings, polyisocyanate hardener (when properly formulated) resists vegetable oils, dairy fats, and cleaning agents (e.g., sodium hypochlorite). It complies with food safety standards (e.g., EU 10/2011) and avoids leaching harmful substances into food.
• Corrosion Protection for Metals: In marine coatings, the cross-linked film from polyisocyanate hardener acts as a barrier against saltwater and humidity, extending the service life of ship hulls by 30–50% compared to non-cured coatings.
Polyisocyanate hardener’s adjustable functionality (e.g., 2–6 isocyanate groups per molecule) allows it to pair with a wide range of resins and substrates, adapting to diverse industrial needs.
• Compatibility with Resin Systems: It forms stable bonds with hydroxyl-functional resins (polyester, polyurethane), epoxy resins (via amine-modified reactions), and even water-based resins (when using hydrophilic polyisocyanates). This flexibility makes it suitable for both solvent-based and water-based coating systems.
• Adhesion to Diverse Substrates:
◦ On metals (e.g., steel, aluminum), it reacts with surface hydroxyl groups to form chemical bonds, preventing delamination.
◦ On plastics (e.g., PVC, ABS), its low viscosity ensures penetration into micro-pores, enhancing mechanical anchoring.
◦ On wood, it cross-links with cellulose hydroxyls, reducing swelling from moisture.
• Customizable Reactivity: By adjusting the NCO content (e.g., 15–25%), manufacturers can tailor curing speed—from fast-setting (for assembly line adhesives) to slow-curing (for large-scale coating projects).
The cross-linked network formed by polyisocyanate hardener imparts exceptional mechanical properties to coatings and adhesives, ensuring long-term performance under stress.
• High Hardness & Abrasion Resistance: In floor coatings for warehouses, polyisocyanate-cured systems achieve a pencil hardness of 3H–4H (per ASTM D3363) and resist wear from heavy forklift traffic—outperforming acrylic coatings (1H–2H) which scratch easily.
• Flexibility & Impact Resistance: For coil coatings (used in metal roofing), the cured film retains 100% flexibility even after 180° bending (per ASTM D522) and withstands impact from hailstones without cracking—critical for outdoor applications.
• Adhesive Shear Strength: In structural adhesives for wind turbine blades, polyisocyanate hardener enhances shear strength to ≥15 MPa (per ASTM D1002), ensuring bonds hold under extreme wind loads.
As industries demand higher efficiency, durability, and versatility in coatings and adhesives, polyisocyanate hardener stands out as a high-performance curing solution. Its fast curing, chemical resistance, broad compatibility, and superior mechanical strength address core needs across automotive, aerospace, construction, and food packaging sectors. By leveraging polyisocyanate hardener, manufacturers not only improve product performance but also adapt to diverse production requirements—driving innovation and reliability in industrial applications.



Sitemap Blog Xml Privacy Policy
Copyright @ Runshine New Materials(FoShan) Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
 Network Supported
Network Supported
leave a message
Scan to wechat :

Scan to whatsapp :

