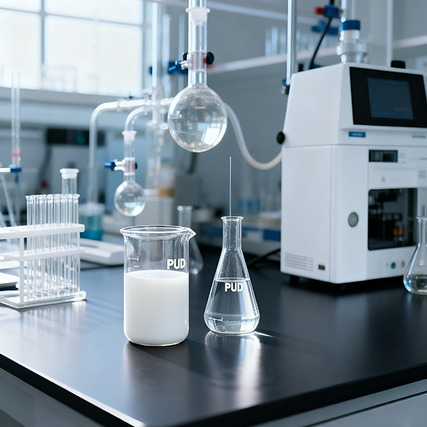
Zero-VOC Waterborne Polyurethane Dispersion (PUD) has become a transformative material in the global coatings industry, combining exceptional performance with strict environmental compliance. Unlike solvent-based polyurethane coatings that rely on volatile organic compounds (VOCs) for dispersion, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD uses water as the primary dispersion medium, resulting in VOC levels below 5g/L—meeting rigorous standards such as the US EPA’s Title V and the European Union’s REACH regulation. This unique composition not only reduces air pollution and health risks but also preserves PUD’s core advantages: excellent adhesion, flexibility, and durability. As industries shift toward sustainable practices, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD has emerged as a preferred choice, with its versatility expanding across architectural, industrial, and consumer goods coatings. Below is a detailed analysis of Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD’s types, application-specific properties, key chemical mechanisms, and future trends—all centered on PUD’s role as a game-changing eco-friendly coating.
--
Types of Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD
The classification of Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD is based on its molecular charge and functional groups, ensuring each variant aligns with specific coating requirements while maintaining Zero-VOC compliance.
Application-Specific Advantages of Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD in Coatings
TZero-VOC Waterborne PUD’s success stems from its ability to address industry-specific challenges while maintaining eco-friendliness. Below are its key applications in the coatings sector, each leveraging unique PUD properties:
1. Architectural Coatings
In architectural coatings, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD delivers a balance of performance and safety. When formulated into wall paints or ceiling coatings, PUD forms a breathable yet moisture-resistant film—thanks to the hydrophilic polyurethane segments in PUD that repel liquid water but allow water vapor transmission. This prevents mold growth in humid environments (e.g., bathrooms, basements). Unlike solvent-based alternatives, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD emits no harmful fumes during application, making it safe for schools, hospitals, and nurseries. Additionally, PUD-based architectural coatings offer excellent color retention: the cross-linked polyurethane network in PUD’s film resists UV-induced degradation, ensuring the coating retains its hue for 5–10 years without chalking or fading.
2. Industrial Metal Coatings
Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD is revolutionizing industrial metal coatings by combining corrosion protection with eco-friendliness. When applied to steel, aluminum, or galvanized metals, PUD forms a dense, cross-linked film that acts as a barrier against oxygen, water, and corrosive ions (e.g., chloride). This PUD’s flexibility prevents film cracking during metal thermal expansion (e.g., automotive engine parts, outdoor HVAC units), a common failure point for rigid solvent-based coatings. Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD also cures at lower temperatures (60–80°C) compared to traditional metal coatings, reducing energy consumption in manufacturing— further enhancing this PUD’s sustainability credentials.
3. Wood & Furniture Coatings
For wood and furniture coatings, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD enhances both aesthetics and durability. This PUD penetrates wood pores slightly, accentuating the natural grain while forming a scratch-resistant film (hardness up to 2H on the pencil scale). Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD dries quickly (touch-dry in 30 minutes, fully cured in 24 hours), shortening production cycles for furniture manufacturers. Unlike solvent-based wood coatings, PUD-based formulations do not yellow over time—preserving the wood’s natural color or painted finish. This makes Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD the preferred choice for high-end furniture, children’s toys, and indoor cabinetry where Zero-VOC compliance and long-term appearance are critical.
Key Chemical Mechanisms Ensuring Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD Performance
The superior performance of Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD in coatings is rooted in its unique chemical structure and behavior:
1. Dispersion Stability of PUD
Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD’s stability relies on the balance between particle charge (anionic/cationic) or hydrophilic segments (non-ionic) and van der Waals forces. PUD particles typically range from 50–300 nm in diameter— a size that ensures tight packing during film formation. Stabilizers adsorbed on PUD particle surfaces prevent aggregation, ensuring consistent coating thickness and gloss. A stable PUD dispersion is critical: any particle clumping would lead to uneven film formation and reduced adhesion.
2. Film Formation of PUD
PUD film formation occurs in three stages: (1) Water evaporation, which concentrates PUD particles; (2) Particle fusion, where PUD particles deform and merge as polyurethane chains diffuse across particle boundaries; (3) Cross-linking, where reactive groups in PUD (e.g., hydroxyl, isocyanate) react to form a three-dimensional network. This cross-linked structure enhances PUD film’s mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and durability— key to its performance in demanding coatings.
3. Zero-VOC Compliance of PUD
Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD achieves low VOC levels by eliminating volatile solvents entirely. Instead of relying on solvents to dissolve polyurethane, PUD uses water and small amounts of non-volatile co-solvents (e.g., glycerol) to aid dispersion. This not only meets global emission standards but also reduces the risk of fire (unlike flammable solvent-based coatings)— a major safety benefit in manufacturing and application.
Future Trends in Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD Coating Technology
As industries demand higher performance and sustainability, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD development is focusing on three key directions:
1. Bio-Based Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD
Research is accelerating the shift to bio-based PUD, using renewable raw materials (e.g., castor oil polyols, soybean oil polyols) instead of fossil fuel-derived polyols. Bio-based Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD reduces carbon footprints by 30–50% compared to conventional PUD and enhances biodegradability— making it suitable for disposable coatings (e.g., packaging) or temporary protective films. This PUD retains all core properties (adhesion, flexibility) while offering a more circular solution.
2. Nanomodified Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD
Incorporating nanomaterials (e.g., nano-silica, graphene oxide) into Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD is a game-changer for high-performance coatings. Nano-silica enhances PUD film’s scratch resistance (up to 4H hardness), while graphene oxide improves corrosion protection for metal coatings. Nanomodified PUD is already used in electronic device coatings (e.g., smartphone casings) and automotive clear coats— where durability and eco-friendliness are equally important.
3. Smart Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD
Smart PUD coatings with functional properties are emerging. For example, self-healing PUD uses microcapsules filled with polyurethane monomers: when the film is scratched, capsules rupture, and monomers react to repair damage. Thermochromic PUD incorporates temperature-sensitive pigments, allowing coatings to change color (e.g., for smart building exteriors). These innovations expand PUD’s application beyond traditional coatings into high-tech sectors.
Conclusion
Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD has redefined eco-friendly coatings by proving that sustainability does not require sacrificing performance. Its diverse types (anionic, cationic, non-ionic) cater to specific substrate needs, while its application across architectural, industrial, and furniture coatings highlights PUD’s versatility. The chemical mechanisms behind PUD’s dispersion stability, film formation, and Zero-VOC compliance ensure its reliability in demanding environments. As bio-based, nanomodified, and smart PUD technologies advance, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD will continue to lead the coatings industry toward a greener future. For manufacturers and end-users alike, Zero-VOC Waterborne PUD is not just a coating material—it is a solution that aligns with global sustainability goals while delivering the performance that modern industries demand. PUD’s role as a cornerstone of eco-friendly coatings is set to grow, shaping the industry for decades to come.



Sitemap Blog Xml Privacy Policy
Copyright @ Runshine New Materials(FoShan) Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
 Network Supported
Network Supported
leave a message
Scan to wechat :

Scan to whatsapp :

